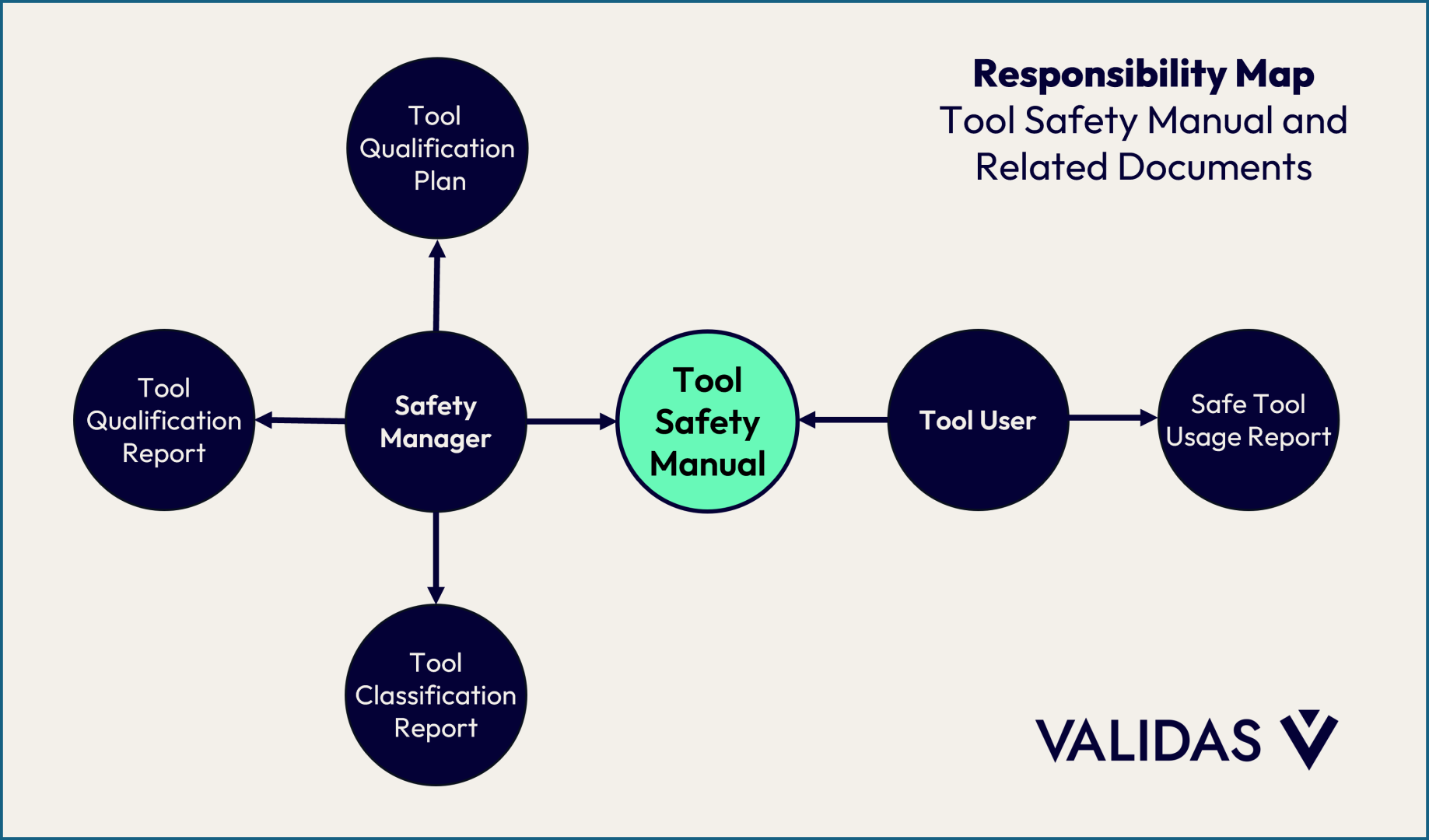
Validas' advanced model-based approach to generating safety documents stems from a deep analysis of tool features, potential errors, inputs, and outputs. By systematically documenting this "error model," using our in-house Tool Chain Analyzer (TCA), we can automatically generate Tool Safety Manuals that are precise, comprehensive (covering necessary mitigations), and yet as concise as possible (thanks to the rigor of qualification).
We believe that clear, concise, and accurate Tool Safety Manuals are fundamental to building safe systems efficiently. They bridge the gap between high-level safety requirements and the daily work of the development team.
The Bottom Line
The Tool Safety Manual is not just a peripheral requirement in tool classification and, if applicable, qualification is a central, essential part of the process. It serves as the practical, user-facing embodiment of all the safety considerations behind the tool. This document directly empowers developers to use complex tools safely and correctly within regulated environments.
Understanding its purpose, adhering strictly to its contents, and having clear processes (and ideally, automated tools) for documenting its usage are essential for compliance, risk reduction, and ultimately, for building trustworthy safety-critical systems. Don't overlook the quiet guardian – your safety depends on it.
Don’t Let the Tool Safety Manual Be Your Blind Spot!
Join Oscar Slotosch in our dedicated podcast episode as he breaks down what makes a Tool Safety Manual effective and why it matters for functional safety.
If you’re ready to go deeper schedule a free consultation and we will review your case and help you understand what's needed.
 Beginner's Guide
Where Do You Start with ISO 26262? The Case for a Tool Readiness Check
Beginner's Guide
Where Do You Start with ISO 26262? The Case for a Tool Readiness Check
 Deep Dive
Tool Qualification for High Risk AI Applications: A Complete Guide to Building Safe, Compliant AI
Deep Dive
Tool Qualification for High Risk AI Applications: A Complete Guide to Building Safe, Compliant AI
 Deep Dive
Static Analysis for Safer C/C++: Avoiding Undefined Behavior and Closing Coverage Gaps
Deep Dive
Static Analysis for Safer C/C++: Avoiding Undefined Behavior and Closing Coverage Gaps